Electric companies typically have 5–10 different rate schedules for their main
customer groups. The average price charged to large industrial users may
differ substantially from that charged to residences. Moreover, many consumers
pay a price for electricity based on the time of day they use it. For
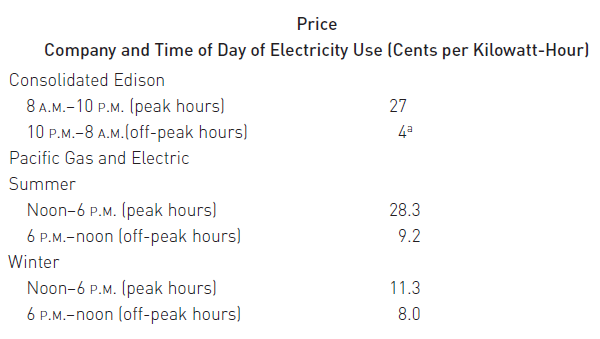
example, the prices charged by Consolidated Edison, a large New York electric
utility, and Pacific Gas and Electric, a major California electric utility, are as
follows:
Electric utilities use their cheapest generators continuously and start up their
more costly ones as demand goes up. Consequently, at 3 a.m., a utility might
meet its requirements from a hydroelectric dam that produces electricity for
$0.02 per kilowatt-hour. However, on a hot day in August, when air conditioners
are running full blast, demand would be so great that the utility would
be forced to use its most costly generators—perhaps an oil-fi red plant where
electricity costs $0.07 per kilowatt-hour.
a. Does price discrimination occur in the market for electricity?
b. Why have some state regulatory commissions, including the Public
Service Commission of New York, ordered that time-of-day rates be
phased in for residential consumers?
c. In many areas, both residential and industrial consumers tend to pay a
lower price per kilowatt-hour if they use more rather than less electricity.
Is this price discrimination? If so, what kind of price discrimination is it?
d. Explain why price discrimination is used by managers of electric companies.
Â
"Looking for a Similar Assignment? Get Expert Help at an Amazing Discount!"


